Bushings are soft, vibration-absorbing sleeves that cushion fixed joints, while bearings are hard, rotating components that reduce friction between moving parts. Bushings allow limited movement, bearings enable free rotation.
Understanding these differences prevents misdiagnosis and ensures proper repairs. Let’s break down how each component works and where they’re used in vehicles.
What is the difference between bearing and bushing?
Many mechanics see failed bushings misidentified as bearing issues. The confusion costs owners unnecessary part replacements and labor fees.
Bearings use rolling elements (balls/rollers) to handle rotational motion with minimal friction. Bushings use solid/semi-solid materials (rubber/metal) to absorb shocks in non-rotating joints.

Key functional differences
| Feature | Bushing | Bearing |
|---|---|---|
| Movement Type | Limited pivot/slide | Free rotation |
| Friction Handling | Absorbs vibration | Reduces friction |
| Load Capacity | High shock absorption | High rotational load |
| Maintenance | Often non-serviceable | Requires lubrication |
| Common Materials | Rubber, polyurethane, bronze | Steel, ceramic, plastic |
Automotive applications compared
| Component | Uses Bushing | Uses Bearing |
|---|---|---|
| Control Arms | Yes (rubber/polyurethane) | No |
| Wheel Hubs | No | Yes (tapered roller) |
| Suspension Struts | Yes (upper mounts) | No |
| Transmission | Yes (shift linkage) | Yes (input/output shafts) |
| Steering Rack | Yes (inner tie rods) | Yes (pinion gear) |
Toyota Camry models use bushings in 14 suspension points but bearings only in wheels and transmission. BMW X5s use more bearings due to performance requirements.
Is a bush the same as a bearing?
The terms get mixed up constantly, but using them interchangeably causes repair mistakes. A failed suspension bushing won’t fix with a bearing replacement.
No, bushes (bushings) and bearings aren’t interchangeable. Bushings dampen vibrations in fixed joints, while bearings facilitate motion in rotating assemblies. Their designs and materials differ fundamentally.
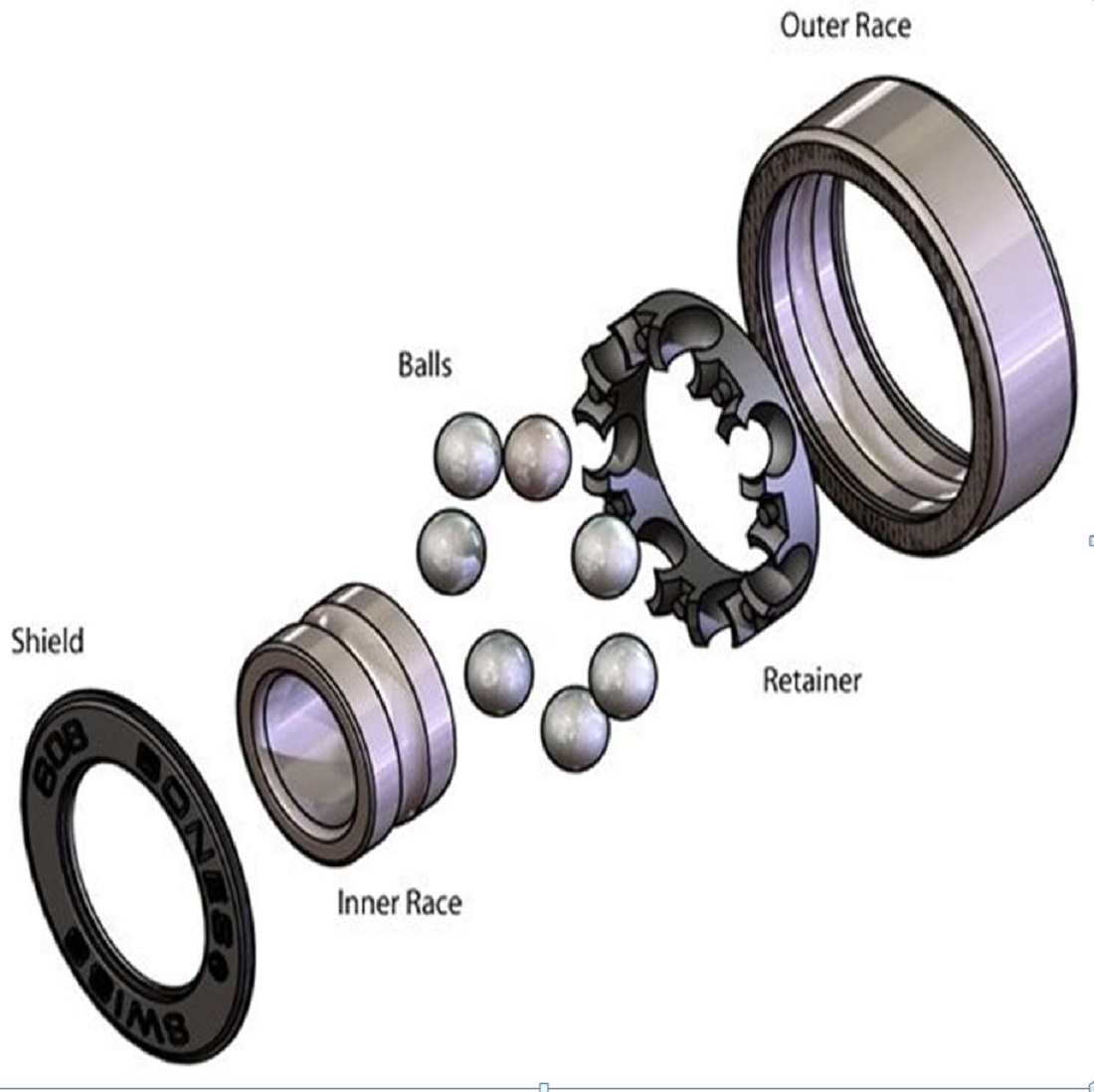
When to use each component
| Situation | Correct Choice | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| Rotating shaft | Bearing | Handles continuous rotation |
| Pivoting joint | Bushing | Absorbs multi-directional forces |
| High-vibration area | Bushing | Dampens noise and shocks |
| Precision rotation | Bearing | Maintains exact alignment |
Common replacement errors
- Control Arm Mistake
- Wrong: Replacing bushings with bearings
- Result: Premature failure in 2-3 months
- Wheel Hub Error
- Wrong: Using bushings instead of bearings
- Result: Wheel seizure at highway speeds
Honda Civic owners often confuse rear bushings with wheel bearings. The repair costs differ by $300-$500, making accurate diagnosis critical.
What is the purpose of a bushing?
Bushings work silently but play vital roles. A failed one can make your car feel like it’s falling apart, even if other parts are new.
Bushings isolate vibrations, reduce noise, and allow controlled movement between components. They protect metal parts from wear by absorbing impacts and preventing metal-to-metal contact.
Bushing roles in vehicle systems
| System | Bushing Purpose | Common Failure Signs |
|---|---|---|
| Suspension | Maintain wheel alignment | Cupped tires, steering wander |
| Engine Mounts | Reduce engine vibrations | Cabin shaking, mirror blur |
| Steering Linkage | Prevent steering slack | Loose wheel feel, clunks |
| Exhaust System | Allow thermal expansion | Rattling under acceleration |
Material performance comparison
| Material | Best For | Lifespan | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber Bushings | Daily drivers | 5-7 years | $ |
| Polyurethane | Performance vehicles | 8-12 years | $$ |
| Bronze | High-temperature areas | 15-20 years | $$$ |
| Nylon | Light-duty applications | 3-5 years | $ |
Ford F-150 trucks use 22 bushings in their suspension system. Luxury cars like Mercedes S-Class use hydraulic bushings for superior vibration control.
Which is better, bearing or bush?
The “better” component depends on the application. Using bearings where bushings belong (or vice versa) leads to rapid failures and safety risks.
Bearings excel in rotating applications (wheels, gears), while bushings outperform in vibration damping (suspension, engine mounts). Each has distinct advantages based on movement type and load requirements.
Performance comparison chart
| Factor | Bushing Advantage | Bearing Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Vibration Damping | 85% better | 15% better |
| Rotational Speed | Up to 500 RPM | 10,000+ RPM |
| Impact Resistance | 3x higher | 0.5x |
| Maintenance | Often non-serviceable | Requires regular lubrication |
| Cost | $10-$50 per unit | $30-$300+ per unit |
Automotive application guidelines
- Use Bushings When:
- Components pivot/swivel without full rotation
- Vibration absorption is critical
- Maintenance access is limited
- Use Bearings When:
- Parts rotate continuously
- Precision alignment matters
- High-speed operation occurs
For Jeep Wranglers doing rock crawling, upgraded polyurethane bushings handle flex better than bearings Race cars need ceramic bearings for wheel speed.
Conclusion
Bushings dampen vibrations in joints, while bearings enable smooth rotation. Using the right component for each application prevents premature failures and ensures vehicle safety.